At a Glance
Mantle's TrueShape technology combines CNC precision with 3D printing for high-quality tool steel components.
Angstrom aims to industrialize and make metal additive technology broadly accessible with financing and design services.
The acquisition may shift Mantle from standalone market strategy to a captive solution within Angstrom's operations.
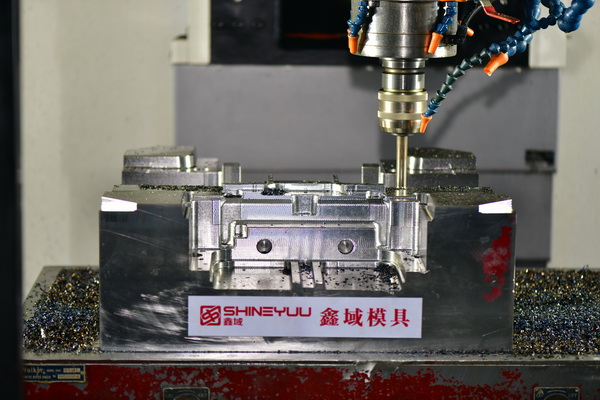
Automotive Tier 1 supplier Angstrom Group has acquired Mantle, a San Francisco–based 3D printing startup specialized in metal tooling. The acquisition announced on Oct. 30, 2025, will expand Mantle’s reach and accelerate adoption of its automated toolmaking technology across global manufacturing markets, said the news release.
By combining Mantle’s metal additive manufacturing system with Angstrom Group’s deep industry expertise and diverse portfolio, the two companies aim to deliver new efficiencies and create opportunities for molders, moldmakers, and OEMs worldwide.
Manufacturing transformation at scale
“Our goal is clear: To industrialize this breakthrough metal additive technology and make it broadly accessible,” said Angstrom Group founder and CEO Nagesh Palakurthi. “By offering financing solutions and integrated tool design services, we will help customers adopt and benefit from advanced metal 3D printing — transforming manufacturing at scale.”
The acquisition by the Angstrom Group will enable Mantle to further its “mission of revolutionizing toolmaking for plastic part manufacturers globally,” added Mantle CEO Ted Sorom. “Toolmakers should expect to see continued innovation and efficiency as Mantle’s TrueShape technology is further advanced and expanded with the full backing of the Angstrom Group.”
Layered approach to tooling fabrication
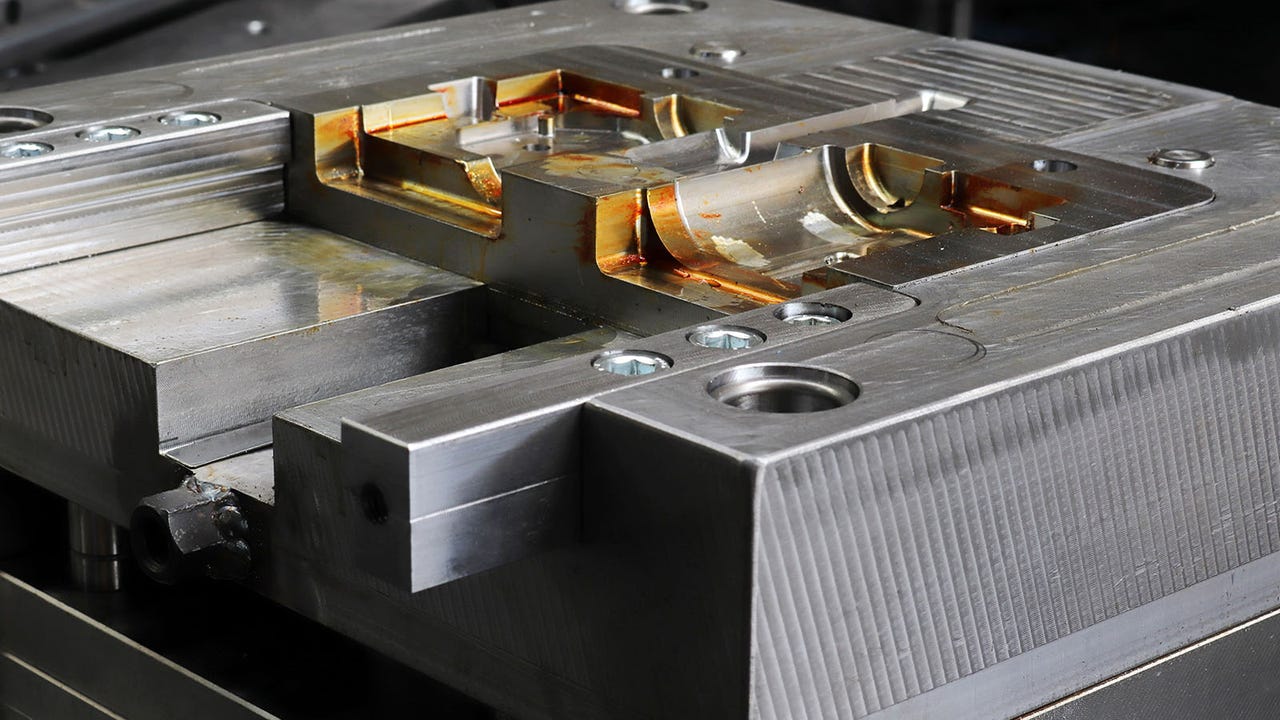
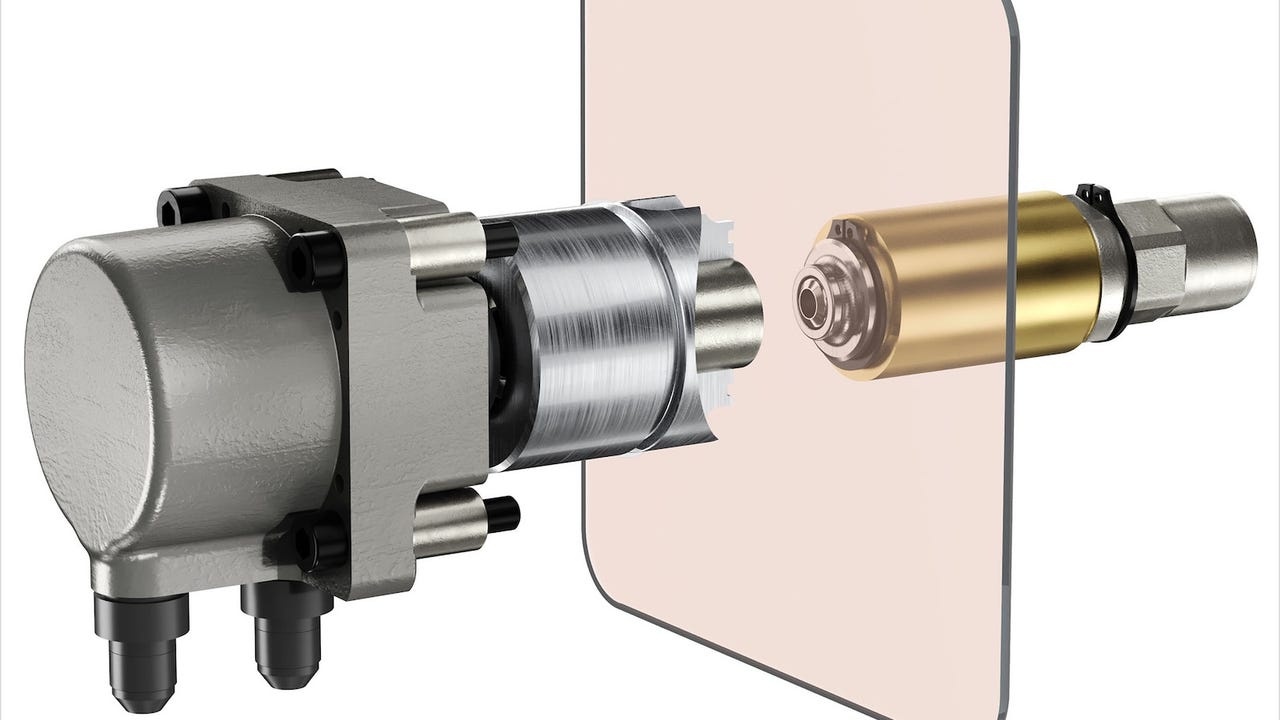
TrueShape technology combines the precision of a CNC machine with the freedom of a 3D printer to deliver the accuracy, surface finish, and tool steel properties required for demanding tooling components, explains Mantle on its website. The company describes the process as follows: The printer deposits a metal paste layer-by-layer to build up a part. Once an entire layer is printed, it is heated to dry paste and made firm enough for machining. High-speed cutting tools machine the part to increase accuracy, improve surface finish, and refine features. Machining the dried paste is significantly faster than machining traditional solid metal. These steps are repeated to build and refine the entire part.
In addition to printing prototyping tools, the process is suitable for fabricating production tooling, according to Mantle. It is compatible with H13 tool steel, which can be heat treated to 52 HRC, enabling excellent wear resistance and millions of cycles, said the company. Conformal cooling can be incorporated, further reducing cycle times and costs.
Competitive mold-making advantage
“An interesting aspect of the acquisition is that Angstrom appears to have acquired Mantle primarily for its own competitiveness as a mold maker,” commented Wohlers Associates, a consultancy powered by ASTM International and focused on the additive manufacturing/3D printing market. “It is not yet clear whether Mantle systems will continue to be commercialized for other injection molding companies. From Mantle’s perspective, the acquisition represents a secure exit as a captive solution within an established global tooling firm — apparently opting not to pursue a standalone market strategy,” said Wohlers.
Founded in 1999 and based in Southfield, MI, Angstrom is a Tier 1 full-service supplier to automotive and industrial OEMs. The company’s operations span 41 locations across North America, South America, and Europe. Its capabilities include metal casting, stamping, forging, tubular forming, machining, and assembly; plastic injection molding; and the fabrication and assembly of electrical components.